Light fixtures (or “luminaires”) control and distribute light in different ways. Shielded light fixtures are among the ways that this can be accomplished. The reasons to use them are as follows:
- Reduce glare
- Diffuse light
- Protect and/or hide lamps
- Enhance fixture appearance
There are three different types of shielded light fixtures:
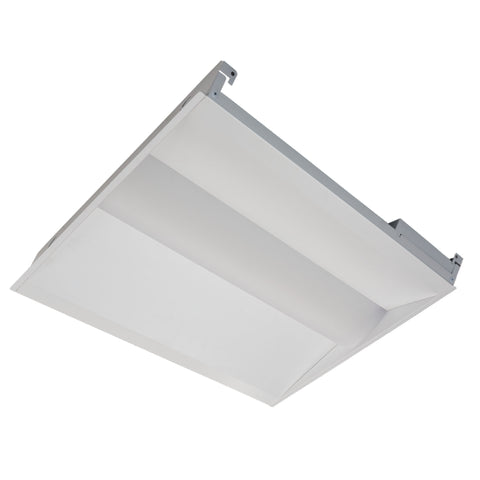
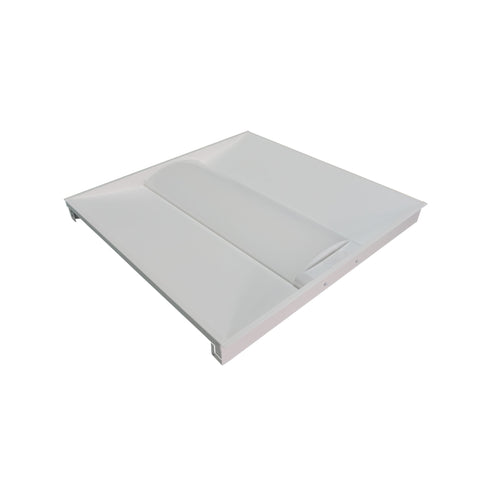
Diffuser – This is a translucent or semi-transparent cover that spreads out or scatters light. Using a diffuser will control brightness and give off a soft light relative to the lamps being used. They are typically made of glass or plastic and are used on the bottom or sides of a light fixture. They are typically used in offices or schools where there is a lower ceiling height.
Here are some examples of fixtures that use diffusers:
Lens – This is a clear or transparent cover. Two types or commonly used lenses are as follows:
Prismatic – These are shaped with an arrangement of small refractive components on one side for excellent light diffusion and glare reduction.
Here are some examples of fixtures that use prismatic lenses:
Polycarbonate – These lenses are extremely durable and are ideal for harsh environments. They are typically used with vapor tight light fixtures used in wet or dusty areas.
Here are some examples of fixtures that use polycarbonite lenses:
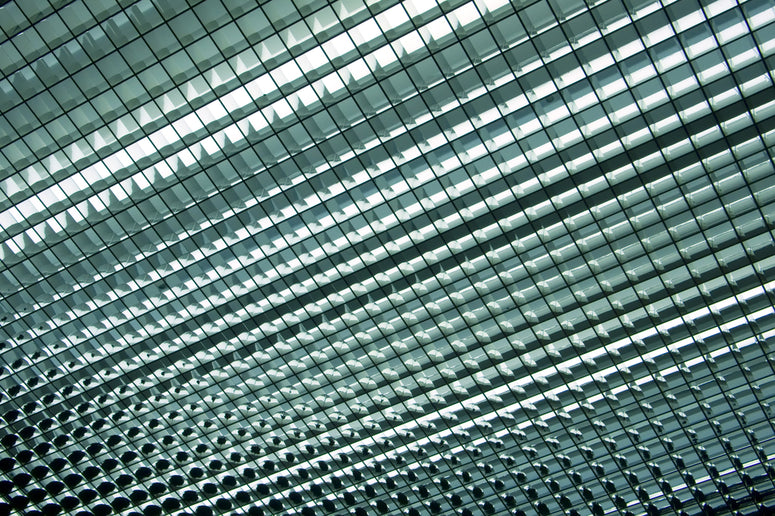
Parabolic Louver – These are baffles that utilize an open grid pattern with parabolic reflectors in each cell of the grid. They are excellent for directing light downward and reducing glare from the fixture. Size and depth of a louver will affect light output and distribution.

 High Bay LED Lighting
High Bay LED Lighting
 Industrial Low Bay Lighting
Industrial Low Bay Lighting
 Industrial Strip Lights
Industrial Strip Lights
 Vapor Tight Lighting
Vapor Tight Lighting
 LED Shop Lights
LED Shop Lights
 Hazardous Area / Explosion Proof Lighting
Hazardous Area / Explosion Proof Lighting
 Loading Dock Lights
Loading Dock Lights
 Construction / Portable Lighting
Construction / Portable Lighting
 Industrial Ceiling Fans
Industrial Ceiling Fans
 LED Work Lights
LED Work Lights
 Networked Controlled Lighting
Networked Controlled Lighting
 NEW Lighting
NEW Lighting
 Clearance
Clearance
 Troffer Lights
Troffer Lights
 LED Flat Panel Lights
LED Flat Panel Lights
 Drop Ceiling Lights
Drop Ceiling Lights
 Suspended LED Lights
Suspended LED Lights
 LED Cylinder Lights
LED Cylinder Lights
 Exit / Emergency
Exit / Emergency
 Wrap Lighting Fixtures
Wrap Lighting Fixtures
 Gooseneck and Barn Lights
Gooseneck and Barn Lights
 Stairway & Corridor Lighting
Stairway & Corridor Lighting
 Hospital Bed Lights
Hospital Bed Lights
 Commercial Sign Lights
Commercial Sign Lights
 Recessed Lighting
Recessed Lighting
 Wafer Lighting
Wafer Lighting
 RGB LED Lights
RGB LED Lights
 Grow Lights
Grow Lights
 UV Disinfecting Lights & Air Purifier Fixtures
UV Disinfecting Lights & Air Purifier Fixtures
 Refrigeration Lighting
Refrigeration Lighting
 LED Flood Lights
LED Flood Lights
 Outdoor Wall Lights
Outdoor Wall Lights
 LED Area Lights
LED Area Lights
 Parking Lot Lights & Poles
Parking Lot Lights & Poles
 Outdoor Post Top Lights
Outdoor Post Top Lights
 LED Stadium Lighting
LED Stadium Lighting
 Canopy Lights
Canopy Lights
 Security & Motion Sensor Lights
Security & Motion Sensor Lights
 LED Bollard Lights
LED Bollard Lights
 Outdoor LED Linear Light Fixtures
Outdoor LED Linear Light Fixtures
 Solar Powered LED Lighting
Solar Powered LED Lighting
 Dusk to Dawn Lights
Dusk to Dawn Lights
 Landscape Lighting
Landscape Lighting
 Outdoor String Lights
Outdoor String Lights
 Coastal Wildlife Lighting
Coastal Wildlife Lighting
 Outdoor House Lights
Outdoor House Lights
 Architectural Linear Lights
Architectural Linear Lights
 Architectural Grid Mount Lights
Architectural Grid Mount Lights
 Architectural Round Pendant Lights
Architectural Round Pendant Lights
 Architectural Square Linear Lights
Architectural Square Linear Lights
 Architectural X-Shaped Linear Lights
Architectural X-Shaped Linear Lights
 Architectural LED Wall Packs
Architectural LED Wall Packs
 Ceiling Fans
Ceiling Fans
 Ceiling Lights
Ceiling Lights
 Chandelier Lights
Chandelier Lights
 Pendant Lighting
Pendant Lighting
 Island Lights
Island Lights
 Track Lighting
Track Lighting
 Under Cabinet Lighting
Under Cabinet Lighting
 Vanity Lights
Vanity Lights
 Wall Sconces
Wall Sconces
 LED Tape Lights
LED Tape Lights
 LED Mirrors
LED Mirrors
 LED Light Bulbs
LED Light Bulbs
 LED Tube Lights
LED Tube Lights
 LED Corn Lights
LED Corn Lights
 Vintage LED Bulbs
Vintage LED Bulbs
 Decorative LED Bulbs
Decorative LED Bulbs
 Fluorescent Light Bulbs
Fluorescent Light Bulbs
 Metal Halide Lamps
Metal Halide Lamps
 LED Magnetic Strip Retrofit Kits
LED Magnetic Strip Retrofit Kits
 LED Strip Light Retrofit Kits
LED Strip Light Retrofit Kits
 High Bay LED Retrofit Kits
High Bay LED Retrofit Kits
 LED Troffer Retrofit Kits
LED Troffer Retrofit Kits
 LED Wall Pack Retrofit
LED Wall Pack Retrofit
 LED Street Light Retrofit Kits
LED Street Light Retrofit Kits
 Recessed Lighting LED Retrofit Kits
Recessed Lighting LED Retrofit Kits
 Ballasts & Drivers
Ballasts & Drivers
 Emergency Ballast For LED & Fluorescent Lights
Emergency Ballast For LED & Fluorescent Lights
 Electrical Supplies & Mounting Kits
Electrical Supplies & Mounting Kits
 Electrical Tools
Electrical Tools
 Switches & Receptacles
Switches & Receptacles
 Electrical Power Cords
Electrical Power Cords
 Sensors and Timers
Sensors and Timers
 Smart Home Automation
Smart Home Automation
 High Bay Occupancy Sensors
High Bay Occupancy Sensors
 Electric Vehicle Chargers
Electric Vehicle Chargers
 Hand Dryers
Hand Dryers
 LED Shop Lights
LED Shop Lights
 Office Lights
Office Lights
 Classroom Lights
Classroom Lights
 Church Lights
Church Lights
 Gym Lighting
Gym Lighting
 Factory Lights
Factory Lights
 Hospital Lights
Hospital Lights
 Walkway Lights
Walkway Lights
 Parking Lot Lights
Parking Lot Lights
 Exterior Building Lights
Exterior Building Lights
 Sports Lighting
Sports Lighting
 Airport Lights
Airport Lights
 NSF Rated Lights
NSF Rated Lights
 Restaurant Lights
Restaurant Lights
 Corridor Lights
Corridor Lights
 Barn Lighting
Barn Lighting